We’re just over midway through the hazy days of summer vacation, and children without access to high quality enrichment opportunities are already slipping behind their wealthier peers. As noted in a recent New York Times article, in addition to the decrease in math proficiency that most kids experience over the break, low-income children also lose more than two months of reading skills—skills they don’t regain during the school year. This compounds the already deep educational disparities found among students of different socioeconomic groups, which can be observed as early as 18 months of age.
Most efforts to address these gaps focus on improving our K-12 educational systems. Yet, children spend an average of 80 percent of their waking time outside of a classroom—a simple, yet startling statistic that highlights the need to explore a broader range of solutions.
As we learned at a recent Brookings event, Urban Thinkscape, an ongoing project from developmental psychologists Kathy Hirsh-Pasek and Roberta Michnick Golinkoff, might be one of those solutions. Drawing on findings from their research on guided play—particularly from interventions like the Ultimate Block Party and The Supermarket Study—the project embeds playful learning activities, such as games and puzzles, into public places where children routinely spend time during non-school hours. Designed by architect Itai Palti, each installation is created with specific learning goals in mind and reflects best practices in psychological research.
With a pilot led by researcher Brenna Hassinger-Das in progress in the West Philadelphia Promise Zone, the project is already revealing important lessons—not only for educators, but for urban planners and policymakers as well.
The first involves the (often under-appreciated) need to work with local residents. Through meetings and focus groups with leaders of community organizations, neighbors, and Promise Zone stakeholders, the team gained a clearer understanding of resident needs, spurred interest in the project, identified potential sites, and improved designs. Residents were brought into the process early, empowered to offer suggestions at several stages, and will continue to be engaged as the project is implemented and assessed.
The upshot? When community members are meaningfully involved—and local wisdom valued—from the onset, residents become invested in the project and feel a sense of ownership of it over the long haul. This not only improves the likelihood that the project will succeed, but also helps foster neighborhood trust and cohesion, and builds social capital that can be applied to future efforts.
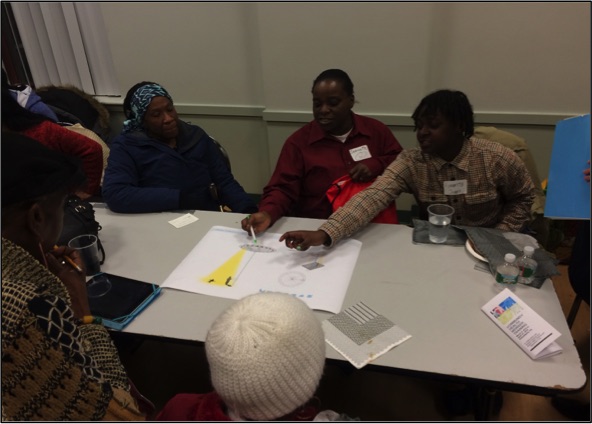

A second lesson is the extent to which a full scaling of the project could help transform distressed neighborhoods through what Project for Public Spaces often refers to as “lighter, quicker, cheaper” interventions.
Many high poverty urban areas are challenged with large numbers of vacant or underutilized properties, as well as dull spaces (like bus stops) that serve only utilitarian functions. The Urban Thinkscape project aims to take such spaces and remake them into opportunities for interaction and learning—and by doing so create tangible improvements to the neighborhood’s physical fabric. While the West Philadelphia pilot has substantial long-term planning behind it, ideally the “playful” installments will be refined over time so they can be more easily and cheaply implemented in other urban neighborhoods.
Finally, the Urban Thinkscape interventions have the potential to advance academic and spatial skills in children, reducing the gap in school readiness, and ultimately fostering better educational and life outcomes.
Many families in high poverty neighborhoods can’t afford extracurricular enrichment activities, particularly during the summer. And even where they might be offered—via community centers, or through other nonprofit initiatives focused on the arts, STEM activities, or sports—children may only experience them at certain times of the week. Urban Thinkscape aims to supplement these activities by embedding learning opportunities into the everyday landscape through interventions that develop numeracy, literacy, and other skills necessary to succeed in school and eventually the workforce. From an urban planning and policy perspective, this individual development is critical to helping build family wealth and vibrant, healthy city neighborhoods.
Though still nascent in its development, the Urban Thinkscape model appears to be a fun, innovative way to give children—and their caregivers—learning opportunities outside the classroom, while creating new gathering spaces and improved public places. In this way, the project is creatively employing the city itself as an agent of change. If the full vision of this work is realized, perhaps we can finally put the brakes on the “summer-slide” such that all kids can start the school year at the top of their game.
The Brookings Institution is committed to quality, independence, and impact.
We are supported by a diverse array of funders. In line with our values and policies, each Brookings publication represents the sole views of its author(s).




Commentary
Cities as classrooms: The Urban Thinkscape project
July 21, 2016