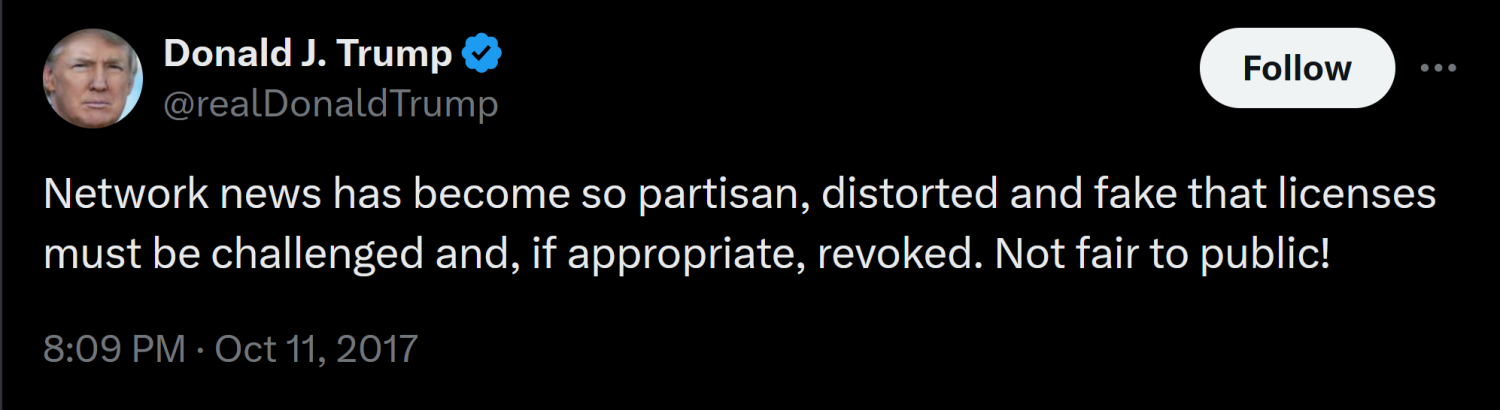
As president of the United States, Donald Trump threatened the federally issued licenses of television broadcast outlets that displeased him. In 2017, after NBC News reported a dispute between the president and his military advisors about the size of the nuclear arsenal, the president launched a series of tweets:
These 2017 tweets did not specifically suggest that he would have the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), which issues the airwave licenses, revoke them on his order. Instead, they appear to echo the 1972 tactics of Richard Nixon, who, displeased by coverage from the Washington Post, encouraged a third party to file a challenge at the FCC (which ultimately went nowhere).
In response to the 2017 tweets, the Trump-appointed chairman of the FCC, Ajit Pai, took a firm stand. “I believe in the First Amendment,” he said. “Under the law, the FCC does not have the authority to revoke a license of a broadcast station based on a particular newscast.”
Now, in 2024, as a presidential candidate, Donald Trump has reasserted that broadcasters who displease him should lose their federal airwave licenses. A September 2023 post on Truth Social accused NBC of “Country Threatening Treason.” He added, “Why should NBC, or any of the other corrupt & dishonest media companies, be entitled to use the very valuable Airwaves of the USA, FREE?”
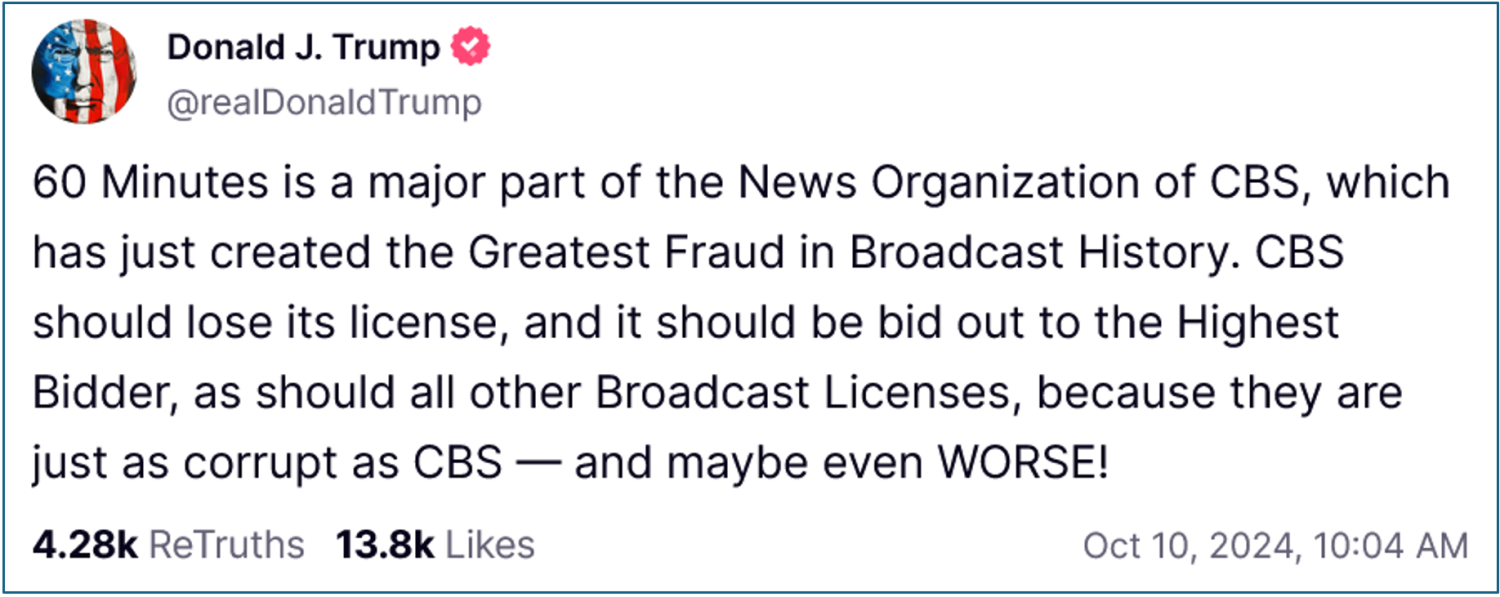
After the moderators of the ABC presidential debate fact-checked his false statements, he called the network “dishonest” and added them to the target list. “To be honest they are a news organization, they have to be licensed. They ought to take away their license for the way they did that,” he said on Fox & Friends. Recently, CBS also came in the crosshairs after he did not like an editing decision in a CBS interview with Kamala Harris. Only weeks before the general election, Mr. Trump again went to Truth Social to expand his targets to include not only CBS, but also “all other Broadcast Licenses.”
The current Chair of the FCC, Jessica Rosenworcel, responded, “the First Amendment is a cornerstone of our democracy. The FCC does not and will not revoke licenses for broadcast stations simply because a political candidate disagrees with or dislikes content or coverage.”
However, the ability of future FCCs to stand up to such instructions could be at risk. Candidate Trump has promised, “I will bring the independent regulatory agencies, such as the FCC and the FTC, back under Presidential authority, as the Constitution demands.” While the Constitution never mentions regulatory agencies, bringing the FCC under direct presidential control would surely undercut its independent decision-making.
But a president of the United States already has powers beyond coercing the FCC. These powers could be exercised not only against broadcasters, but also against those who operate the internet.
The “Doomsday Book”
During his presidency, Donald Trump asserted, “When somebody’s president of the United States, the authority is total.” Whether or not presidential authority is “total,” there does already exist a compendium of presidential powers that have been enacted by Congress for use in extreme circumstances.
Reportedly locked in a White House safe are the secret “Presidential Emergency Action Documents” (PEADs). Colloquially known as the “Doomsday Book,” they are a collection of powers authorized by Congress for the president to use in emergencies. Included in this compendium is Section 706 (codified as 47 USC 606), titled, “War Emergency – Powers of the President,” that is tucked away at the end of the Communications Act of 1934, the statute that created the FCC.
TIME Magazine reports, “When Donald Trump was in the Oval Office, members of the national security staff actively worked to keep him from learning the full extent of these interpretations of presidential authority, concerned he would abuse them.”
Here is what Section 706 authorizes:
(c) Upon proclamation by the President that there exists war or a threat of war, or a state of public peril or disaster or other national emergency… the President, if he deems it necessary in the interest of national security or defense, may suspend or amend, for such time as he may see fit, the rules and regulations applicable to any or all stations or devices capable of emitting electromagnetic radiations within the jurisdiction of the United States as prescribed by the Commission, and may cause the closing of any station for radio communication…
The next subsection, using similar “national security” criteria, gives the president authority over the wired networks, such as those that carry telephone and internet service. Section 706(d), in pertinent part, authorizes the president to “suspend or amend the rules and regulations applicable to any or all facilities or stations for wire communication… cause the closing of any facility or station for wire communication… [or] authorize the use or control of any such facility or station… by any department of the Government under such regulations as he may prescribe…”
The terms “war or a threat of war, or a state of public peril or disaster or other national emergency” are not defined by the Communications Act. Such declarations of national emergency were, however, a go-to solution when Donald Trump was in office. The effort to restrict travel from majority-Muslim countries was justified on national security grounds. Tariffs were levied on foreign steel and aluminum as a national security threat based on their impact on domestic production. When Congress would not give him the funding he wanted for the Mexican border wall, the president simply used a national emergency declaration to reallocate Defense Department funds to build the wall. Reportedly, he even considered declaring that the use of natural gas for electricity production was a national security risk because the gas pipelines could become terrorist targets.
The power of the Chief
Candidate Trump, in September 2023, posted that NBC and other “corrupt & dishonest media companies” are “a true threat to democracy and are, in fact, THE ENEMY OF THE PEOPLE!” He declared, “The Fake News Media should pay a big price for what they have done to our once great Country.”
A 2021 report by the nonpartisan Congressional Research Service (CRS) concluded, “in the American governmental experience, the exercise of emergency powers has been somewhat dependent on the Chief Executive’s view of the presidential office.” When he was Chief Executive, Donald Trump explained how he viewed the office: “I have Article II [of the Constitution], where I have the right to do whatever I want as president.”
The tools to do whatever the president wants—whether at the FCC or in the Doomsday Book—are at hand. As the CRS report concluded, such decisions are dependent “on the Chief Executive’s view of the presidential office.”
The institution that created these broad powers, the Congress, has an important role as overseer of the authority they have delegated to the executive. Congress constantly holds oversight hearings on the agencies of the executive branch; hearings on the unilateral powers granted to the president are warranted. The threshold question for such hearings should be whether there are sufficient guardrails in place to protect against their abuse, and what such protections should look like. Regardless of who wins the election—Congress should review whether the unilateral powers granted to the president in the 20th century need updating for the 21st century.
The Brookings Institution is committed to quality, independence, and impact.
We are supported by a diverse array of funders. In line with our values and policies, each Brookings publication represents the sole views of its author(s).









Commentary
Donald Trump has threatened to shut down broadcasters, but can he?
October 29, 2024