In May, we released a short Brookings report showing which families are most likely to get voucher funding through Arizona’s now-universal Empowerment Scholarship Account (ESA) program. The analysis isn’t complicated, and the results couldn’t be much clearer. A highly disproportionate share of Arizona’s ESA recipients come from the state’s wealthiest and most educated areas. That’s an important finding, even beyond Arizona, since this program is at the forefront of a wave of universal voucher initiatives that’s currently sweeping across red states (and some purple states). What happens with Arizona’s program could foreshadow what’s to come in many parts of the country.
These universal (or near-universal) programs are much more threatening to public education systems than the smaller, more targeted voucher programs that preceded them. They raise concerns about fundamental issues such as civil rights protections and the separation of church and state. Early research and reporting points to ballooning state budgets, wasteful spending, and tuition increases from opportunistic private schools. Meanwhile, hardly anything in the academic literature suggests that universal ESA programs will improve student performance. And yet, the push to remake the U.S. education system in the form of universal school voucher programs continues.
Having entered the fray with our own analysis of a universal ESA program, we’ve gotten a close look at the information environment surrounding these recent initiatives. Suffice to say, it isn’t healthy, at least if we hope for a functional policymaking process. A network of pro-voucher interest groups, think tanks, funders, and politicians are filling an information vacuum with misleading data, faulty or disingenuous arguments, and advocacy that masquerades as research.
Here, we’ll respond to four critiques we’ve heard from that crowd. Part of our goal is to show why their specific critiques of our work are baseless, misleading, or just kind of odd. In doing so, we also hope to illuminate how dangerous the information environment surrounding universal ESAs has become now that many state leaders are dragging their education systems into uncharted territory based on little more than ideology, political calculation, and a fingers-crossed hope that the voucher advocates aren’t leading them astray.
Here are the critiques:
Critique 1: We got our analysis wrong because someone else found something different
Our main results are probably best summarized by Figure 1, below, which appeared in our original post.
The Arizona ZCTAs (ZIP codes, basically) with the lowest poverty rates have the highest share of school-age children who received an ESA. The ZCTAs with the highest poverty rates have the lowest rates of ESA take-up. It’s an extremely straightforward analysis, and we provide a detailed description of what we did in the piece.
Before we published our post, an organization called the Common Sense Institute (CSI) of Arizona—a “non-partisan research organization” with several staff members from former governor Doug Ducey’s administration—looked into a similar question. CSI’s chart, below, tells a completely different story from our chart.
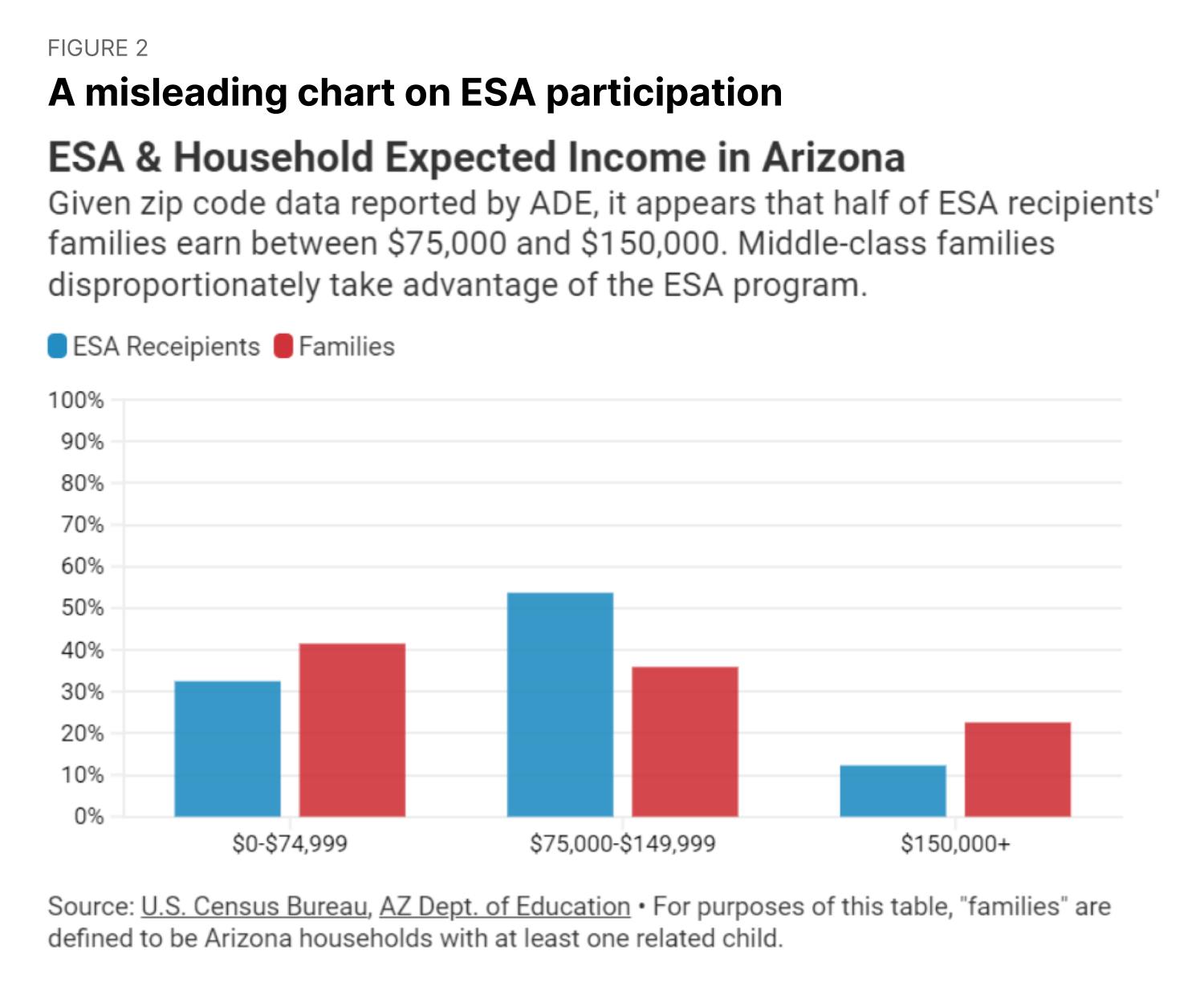
CSI makes it look like relatively few wealthy families in Arizona get ESAs. So, why the discrepancy?
It’s because CSI presented an apples-to-oranges comparison that’s bound to tell that story. The data issue is subtle, but they present ZIP code-level data for ESA recipients (blue bars, on the left) and household-level data for families (red bars, on the right). Many households in Arizona make $150,000 or more, so the far-right, red bar is quite tall. However, few ZIP codes have enough households earning more than $150,000 that the median household income rises above that threshold. As a result, many ESA recipients who earn more than $150,000 aren’t included in the $150,000+ category in this chart. Instead, these households—which earn more than $150,000 themselves but live in ZIP codes where the median income is below $150,000—are included in one of the other blue bars.
Maybe that’s an innocent mistake, but it’s certainly not an accurate representation of which Arizona residents are getting ESAs.
Critique 2: We didn’t place Arizona’s ESA program in the proper context of its other school choice programs
Education Next published an article from Jason Bedrick of the Heritage Foundation that accuses us of omitting key context that, if presented, would markedly change the takeaways from our analysis. Bedrick points out that Arizona’s universal ESA program exists alongside several tax-credit scholarship programs (true) and that families are prohibited from participating in the ESA and tax-credit scholarships simultaneously (also true). He then shares a few numbers, does some hand-waving, and concludes that our “fatally flawed” analysis is deeply misleading because of this omission.
Curiously, Bedrick doesn’t show the relative size of the ESA and tax-credit scholarship programs in Arizona. Here’s the obvious chart to illustrate that comparison—one that EdNext maybe could have requested before publishing yet another round of Heritage Foundation talking points on ESAs:
These tax-credit scholarship (TCS) programs are small relative to a large-and-growing universal ESA program that’s projected to exceed $900 million this year. On top of that, most TCS dollars are going to recipients above 185% of the federal poverty level—the threshold for reduced-price lunch eligibility. (One note: the most recent numbers available for the ESA program come from FY24, while the most recent numbers available for TCS programs come from FY23.)
In other words, this critique—which really isn’t about the universal ESA program we analyzed in the first place—doesn’t even point to context that meaningfully changes the interpretation of our data.
It’s important to emphasize, too, that our analysis was primarily about the high-income households that are obtaining a disproportionate share of Arizona’s ESAs. In that post, we tried to present data in the most straightforward, defensible way possible. If our goal had been to present the most damning data possible, there’s more we’d have said.
Here’s a doozy of an example. According to U.S. Census Bureau data, Arizona has 300 ZCTAs with at least 250 children under age 18. (The other 60 ZCTAs are smaller, which makes them difficult to analyze.) Of those 300 ZCTAs, the one with the single-highest take-up rate for ESAs (236 of every 1,000 children) is the one with the single-highest median household income (about $173,000).
Critique 3: Arizona’s ESA program is too new to assess who will participate
Maybe the most peculiar response we’ve seen is from Mike McShane of EdChoice, who published an op-ed in Forbes.
McShane appeals to Everett M. Rogers’ “diffusion of innovation” theory, which suggests that new technologies and ideas are adopted sequentially by different groups (from early adopters to laggards). McShane asserts that we should expect wealthier and more educated families to be the early adopters of a universal ESA program. He implores us to “think of the first people to own a personal computer, or a cell phone. They started with tech nerds and the wealthy, and eventually worked their way to everyone else.”
Let’s play a game of “one of these things is not like the others” with personal computers, cell phones, and a universal ESA program. Yes, we’d expect wealthier families to be the first to buy computers and cell phones. Those things cost a lot of money. A universal ESA program gives you money. We might expect poorer families—with fewer resources and potentially worse public-school options—to jump first at that opportunity. Even the usual dynamic of uneven information diffusion is complicated in this context, as the ESA program was available to families with children in low-rated schools long before it became universal.
Regardless, there’s reason for concern that vouchers will be more exclusively adopted by the wealthy over time. Jason Fontana and Jennifer Jennings studied the early implementation of a universal ESA account in Iowa. They found that private schools responded to ESA eligibility by increasing their tuition. If this response continues to play out, we might see desirable private schools becoming unaffordable to low-income families that cannot cover a growing gap between the value of their voucher and cost of enrollment. In the long term, this creates a risk of extreme stratification across the public and private sectors.
Chile may provide a glimpse of that potential future. In a 2006 paper in the “Journal of Public Economics”, Chang-Tai Hsieh and Miguel Urquiola analyzed a universal voucher program in Chile. They found suggestive evidence that “the main effect of unrestricted school choice was an exodus of ‘middle-class’ students from the public sector… [which] had a major effect on academic outcomes in the public sector.” These patterns, along with widening achievement gaps between rich and poor, led Chile to drastically modify that program.
Critique 4: We’re targeting ESA programs when the real villains are public schools
A fourth set of critiques presents more conceptual arguments about education reform. Perhaps the most data-infused of these comes from The Goldwater Institute, which notes that Arizona spends a great deal of money to “subsidize public school instruction” for wealthy families. It accuses us (and/or others) of a double standard in how we object to using government funds to pay for wealthy students’ private schooling but not public schooling.
We think this critique reveals just how far the rhetoric surrounding universal ESAs has drifted from Americans’ traditionally held views about education. Americans have long accepted—in fact, embraced—a double standard for public and private schools. Our public education system, with all its flaws, has been a foundational institution for supporting the country’s economic, social, and democratic well-being. Americans have found a rough consensus on how to approach K-12 education: provide free public schooling to everyone (including the wealthy!), allow families to pay for private education if they’d like to opt out of the public system, and maybe create a few opt-out opportunities via school choice policy for those unable to pay.
We’ve entered a period in which conservative lawmakers are confronted with legacy-defining decisions about whether to abandon that long tradition and embrace universal vouchers at the risk of kneecapping their states’ public education systems. Worse, they’re doing it in a polluted information environment that has plenty of loud voices but hardly any credible research to guide or support their decision-making. Now that a few states—including Arizona—have taken that risky leap of faith, the least we can ask of other state leaders is to wait and see what happens.
Editor’s Note: We made a few minor edits on the date this was published to reflect the most recent version of the authors’ text.







Commentary
Be wary of what you read in the school voucher debate
June 13, 2024